
#Subnet mask table class a 64 bits
In IPv6, however, the interface identifier has a fixed size of 64 bits by convention, and smaller subnets are never allocated to end users.ĬIDR encompasses several concepts. Whereas classful network design for IPv4 sized the network prefix as one or more 8-bit groups, resulting in the blocks of Class A, B, or C addresses, under CIDR address space is allocated to Internet service providers and end users on any address-bit boundary. This division is used as the basis of traffic routing between IP networks and for address allocation policies.

IP addresses are described as consisting of two groups of bits in the address: the most significant bits are the network prefix, which identifies a whole network or subnet, and the least significant set forms the host identifier, which specifies a particular interface of a host on that network. Its goal was to slow the growth of routing tables on routers across the Internet, and to help slow the rapid exhaustion of IPv4 addresses. The Internet Engineering Task Force introduced CIDR in 1993 to replace the previous classful network addressing architecture on the Internet. That will give you up to 14 networks shared among 14 hosts (nodes).Method for IP address allocation and routingĬlassless Inter-Domain Routing ( CIDR / ˈ s aɪ d ər, ˈ s ɪ-/) is a method for allocating IP addresses and for IP routing. So to give us 16 possible network numbers, 2 of which cannot be used:. Look at this because you will always come across it during subnetting

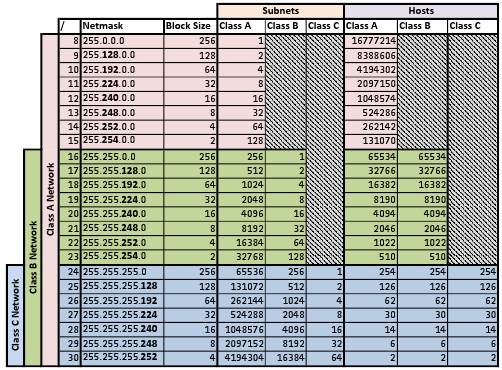
This will limit us to 196 nodes (hosts) on the network instead of 254 we would have without subnetting. You can do this by subnetting this network with a subnet address.Īll you have to do is, try to create 14 subnets of 14 nodes (hosts) each. Given a class C network address of 192.168.1.0, as a network administrator, you need to utilize this network address across multiple small groups within the organization. With these three bits, it is possible to create eight subnets. In order to subnet a network address, The subnet mask has to be extended, using some of the bits from the host ID portion of the address to create a subnetwork ID.įor example, given a Class C network of 192.17.5.0 which has a natural mask of 255.255.255.0, you can create subnets in this manner:ġ92.17.5.0 – 11000000.00010001.00000101.00000000Ģ55.255.255.224 – 11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000īy extending the mask to 255.255.255.224, you have borrowed three bits (indicated by “sub”) from the original host portion of the address and used them to create subnets. It helps to control network traffic due to collisions of packets transmitted by other nodes (host) on the same segment.
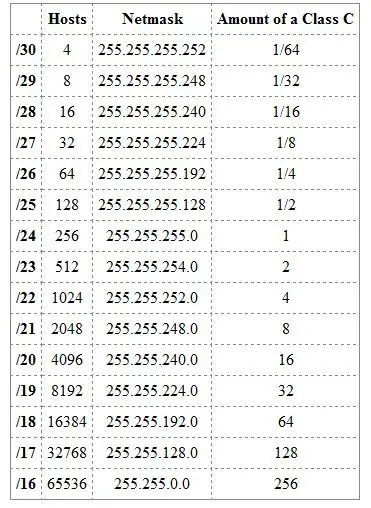
It helps in the preservation of address space in other not to waste addresses.Ĭ. IP Subnet allows you to create multiple logical networks that exist within a single Class A, B, or C network.Ī.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
